Publications
This page is also woefully out of date! Please see a full list of publications and recent preprints on PubMed and Google Scholar.
2017 & earlier below:
J.Y. Sim, M.P. Haney, S.I. Park, J.G. McCall, J.-W. Jeong. Microfluidic neural probes: In vivo tools for advancing neuroscience, Lab on a Chip 10.1039/C7LC00103G (epub ahead of print). (REVIEW)
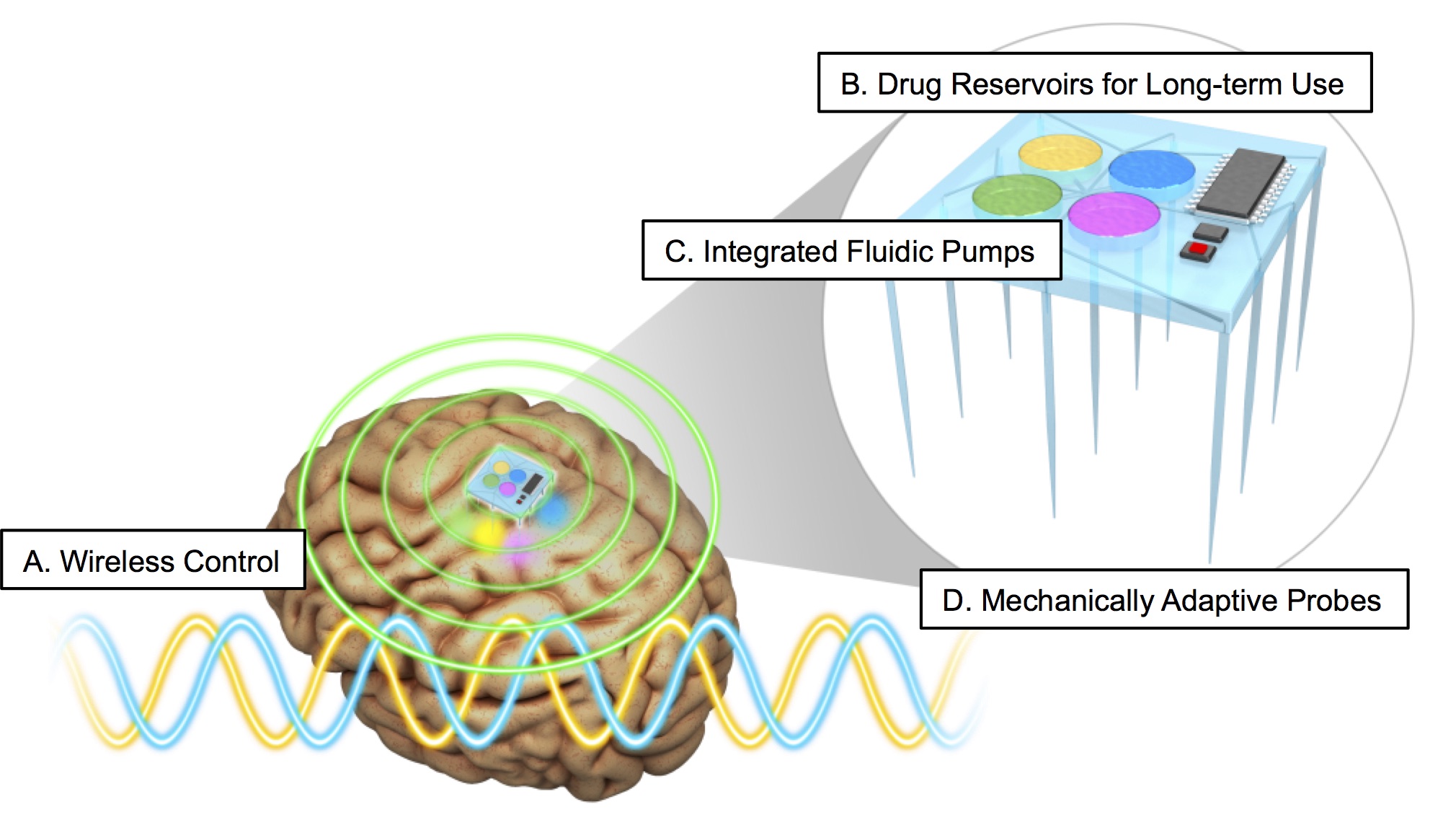
J. G. McCall, R. Qazi, G. Shin, S. Li, M. H. Ikram, K.-I. Jang, Y. Liu, R. Al-Hasani, M. R. Bruchas*, J.-W. Jeong*, J. A. Rogers*, Preparation and implementation of optofluidic neural probes for in vivo wireless pharmacology and optogenetics, Nature Protocols 12(2): 219-237 (2017).
G. Shin, Y.R*. Jeong*, A.M. Gomez*, J. Kim*, R. Al-Hasani*, Z. Xie, A. Banks, J. Kurniawan, J. Tureb, Z. Guo, S.Y. Han, C.J. Yoo, J.-L. Lee, S.H. Lee, J. Yoon, S.-I. Park, S.Y. Bang, V. Samineni, A. Mickle, J.G. McCall, P.T. Pan, T.-i. Kim, J.K. Kim, Y. Li, Y. Huang, R.W. Gereau IV, M.R. Bruchas*, J.S. Ha*, J.A. Rogers*. A low cost, fully implantable optoelectronics technology with near-field wireless operation for broad application in optogenetics, Neuron, 93: 509-521 (2017).
S.I Park, G.Shin, J.G. McCall, R. Al-Hasani, A.J. Norris, L. Xia, D.S. Brenner, K.N. Noh, S.Y. Bang, D.L. Bhatti, K.I. Jang, S.K. Kang, A.D. Mickle, R.W. Gereau IV, M.R. Bruchas, J.A. Rogers. Stretchable multi-channel antennas in soft wireless optoelectronic implants for optogenetics, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(50):E8169–8177 (2016).
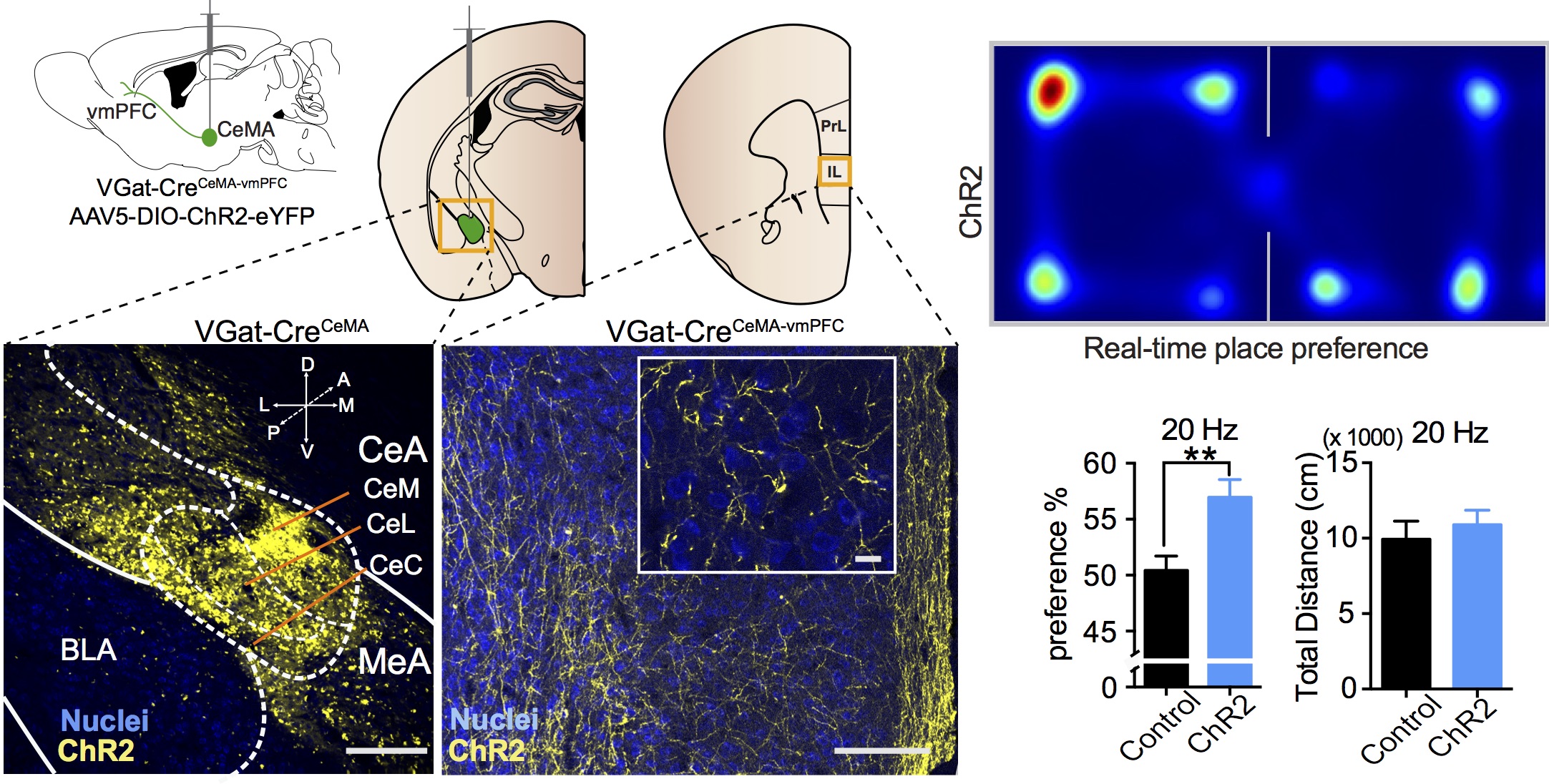
D.-O. Seo, S.C. Funderburk, D.L. Bhatti, L. Motard, D. Newbold, K. Girven, J.G. McCall, M.J. Krashes, D.R. Sparta, M.R. Bruchas. A GABAergic projection from the centromedial nuclei of the amygdala to ventromedial prefrontal cortex modulates reward behavior, Journal of Neuroscience, 36 (42): 10831-10842 (2016).
M.V. Valtcheva*, B.A. Copits*, S. Davidson, T.D. Sheahan, M.Y. Pullen, J.G. McCall, K. Dikranian, R.W. Gereau IV. Human sensory neurons: surgical extraction of dorsal root ganglia and preparation of primary cultures for functional studies. Nature Protocols (10):1877-88 (2016). doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.111.
E.R. Siuda, R. Al-Hasani, J.G. McCall, D.L. Bhatti, M.R. Bruchas. Chemogenetic and Optogenetic Activation of Gαs Signaling in the Basolateral Amygdala Induces Acute and Social Anxiety-Like States, Neuropsychopharmacology 41, 2011–2023 (2016).
N.A. Crowley, D.W. Bloodgood, J.A. Hardaway, A. Kendra, J.G. McCall, R. Al-Hasani, N.M. McCall, Z.L. Schools, M.J. Krashes, B.B. Lowell, J.L. Whistler, M.R. Bruchas, T.L. Kash. Dynorphin controls the gain of an amygdalar anxiety circuit, Cell Reports 14(12):2774-83 (2016).
S.K. Kang*, R. Murphy*, S.W. Hwang*, D.V. Harburg*, N.A. Kruger, P. Gamble, H. Cheng, S. Yu, Z. Liu, J. Shin, J.G. McCall, M. Stephens, H. Ying, G. Park, R.C. Webb, C.H. Lee, S. Chung, D.S. Wie, A. Gujar, A.H. Kim, K.M. Lee, J. Cheng, Y. Huang, P.V. Braun, Z. Ray, J.A. Rogers. Bioresorbable silicon electronic sensors for the brain, Nature 530(7588): 71-6 (2016).
S.I. Park, G. Shin, A. Banks, J.G. McCall, E.R. Siuda, M.J. Schmidt, C. Mazuski, E.D. Herzog, M.R. Bruchas, J.A. Rogers. Ultraminiaturized Photovoltaic and Radio Frequency Powered Optoelectronic Systems for Wireless Optogenetics, Journal of Neural Engineering. 12, 056002 (2015).
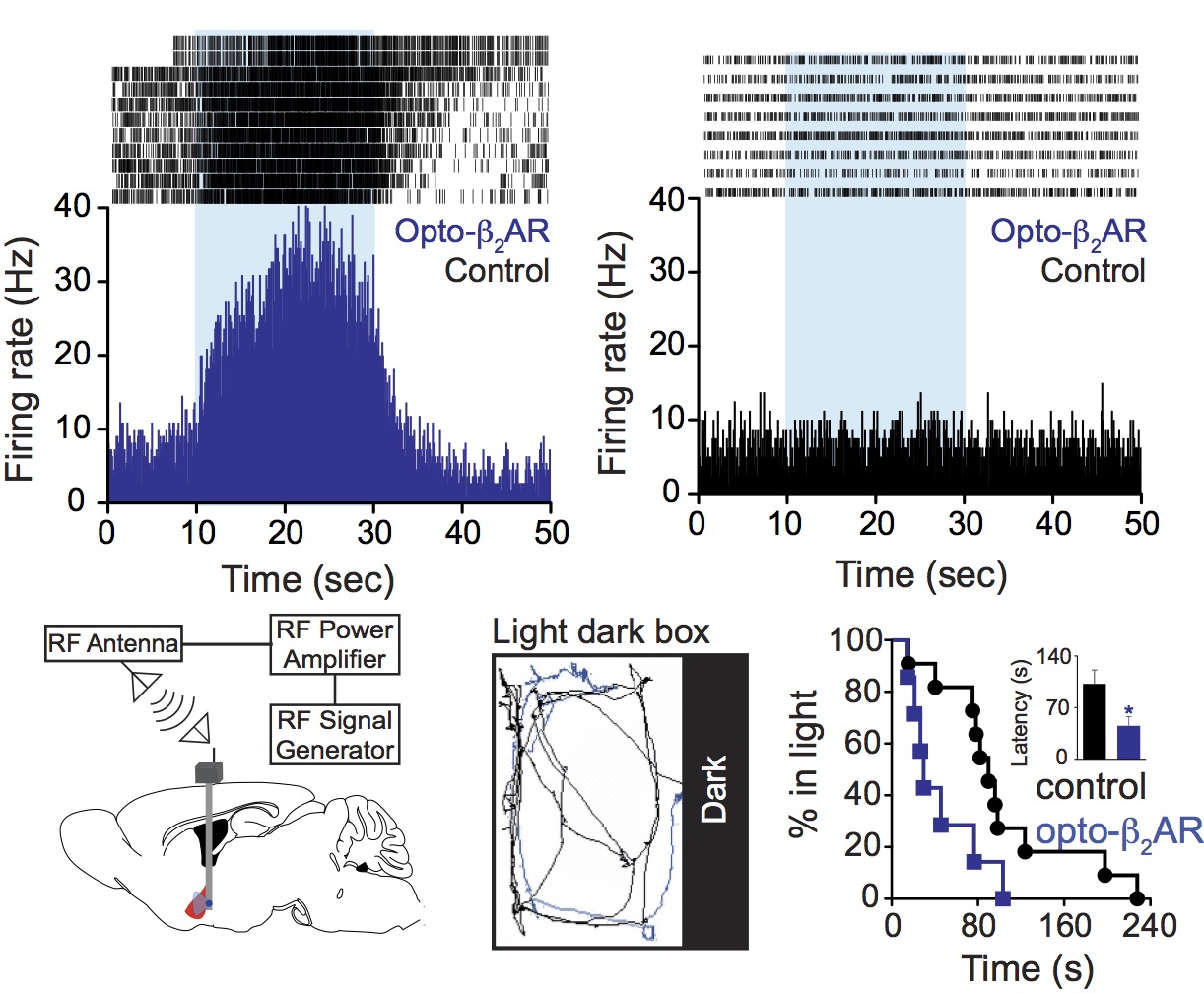
E.R. Siuda, J.G. McCall, R. Al-Hasani, G. Shin, S.l. Park, M.J. Schmidt, S.L. Anderson, W.J. Planer, J.A. Rogers, M.R. Bruchas. Optodynamic simulation of b-adrenergic receptor signaling, Nature Communications 6:8480 (2015).
S.E. Schindler, J.G. McCall, P. Yang, K.L. Hyrc, M. Li, C.L. Tucker, J.M. Lee, M.R. Bruchas, M.I. Diamond. Photo-activatable Cre recombinase regulates gene expression in vivo, Scientific Reports. 5: 13627 (2015). #9 on Scientifica’s “Top 10 discoveries in 10 years of optogenetics”.
R. Al-Hasani*, J.G. McCall*(co-first author), G. P. Schmitz, G. Shin, J.M. Bernardi, D.Y. Hong, N.A. Crowley, M.J. Krashes, B.B. Lowell, T.L. Kash J.A. Rogers, M.R. Bruchas. Distinct subpopulations of nucleus accumbens dynorphin neurons drive aversion or reward, Neuron 87, 1063-77 (2015). Recommended on F1000Prime.
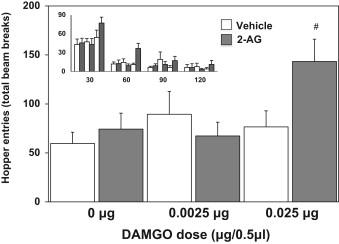
K.E. Parker, J.G. McCall, S.R. McGuirk, S. Trivedi, D.K. Miller, M.J. Will. Effects of co-administration of 2-arachidonylglycerol (2-AG) and a selective µ-opioid receptor agonist into the nucleus accumbens on high-fat feeding behaviors in the rat, Brain Research 1618, 309-315 (2015).
J.G. McCall, R. Al-Hasani, E.R. Siuda, D.Y. Hong, A.J. Norris, C.P.Ford, M.R. Bruchas. CRH engagement of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system mediates stress-induced anxiety, Neuron. 87, 605-620 (2015). Commentary in Neuron.
J.W. Jeong*, J.G. McCall*(co-first author), G. Shin, Y. Zhang, R. Al-Hasani, M. Kim, S. Li, J.Y. Sim, D.Y. Hong, Y. Shi, G. P. Schmitz, L. Xia, Z. He, P. Gamble, Z. Ray, Y. Huang, M.R. Bruchas, J.A. Rogers. Wireless optofluidic systems for programmable in vivo pharmacology and optogenetics, Cell. 162, 662-674 (2015). Commentary in Cell Systems; #5 on Scientifica’s “Top 10 discoveries in 10 years of optogenetics”.
E.R. Siuda*, B.A. Copits*, M.J. Schmidt*, M.A. Baird*, R. Al-Hasani, W.J. Planer, S.C. Funderburk, J.G. McCall, R.W. Gereau IV, M.R. Bruchas. Spatiotemporal control of opioid signaling and behavior, Neuron 86, 923-935 (2015). Commentary in Neuron; #2 on Scientifica’s “Top 10 discoveries in 10 years of optogenetics”.
G. S. Portugal*, R. Al-Hasani*, A.K. Fakira*, J.L. Gonzalez-Romero, Z. Melyan, J.G. McCall, M.R. Bruchas, J.A. Morón. Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation Is Disrupted during Expression and Extinction But Is Restored after Reinstatement of Morphine Place Preference, Journal of Neuroscience 34, 527–538 (2014).
J.G. McCall*(co-first author), T.-I. Kim*, G.C. Shin*, Y.H. Jung, X. Huang, R. Al-Hasani, F. Omenetto, M.R. Bruchas, J.A. Rogers. Fabrication of flexible, multimodal light-emitting devices for wireless optogenetics, Nature Protocols. 8, 2413–2428 (2013). Cover article.
R. Al-Hasani, J. G. McCall, A. M. Foshage, M. R. Bruchas. Locus coeruleus kappa-opioid receptors modulate reinstatement of cocaine place preference through a noradrenergic mechanism, Neuropsychopharmacology. 38, 2484–2497 (2013).
Y. Li.*, X. Shi*, J. Song, C. Lu, T.-I. Kim, J.G. McCall, M.R. Bruchas, J.A. Rogers, Y. Huang. Thermal analysis of injectable, cellular-scale optoelectronics with pulsed power, Proceedings of the Royal Society A 469, 20130142–20130142 (2013).
R. Al-Hasani, J. G. McCall, M. R. Bruchas. Exposure to chronic mild stress prevents kappa opioid-mediated reinstatement of cocaine and nicotine place preference, Frontiers in Pharmacology 4 (2013), doi:10.3389/fphar.2013.00096.
T.-I. Kim*, J.G. McCall* (co-first author), Y.H. Jung, X. Huang, E.R. Siuda, Y. Li, J. Song, Y.M. Song, H.A. Pao, R.-H. Kim, C. Lu, S.D. Lee, I.S. Song, G.C. Shin, R. Al-Hasani, S. Kim, M.P. Tan, Y. Huang, F. Omenetto, J.A. Rogers, M.R. Bruchas. Injectable, Cellular-Scale Optoelectronics with Applications for Wireless Optogenetics. Science, 340(6129), 211-6 (2013).
K.E. Parker, J.G. McCall, M.J. Will. Basolateral amygdala opioids contribute to increased high-fat intake following intra-accumbens opioid administration, but not following 24-h food deprivation. Pharmacology, biochemistry, and behavior, 97(2), 262-6 (2010).